GARDASIL®9 for Women
GARDASIL®9 is a vaccine that helps protect girls, women and individuals with a cervix against 9 HPV types that can lead to certain HPV-related cancers and diseases.

Signs and symptoms of HPV in women
Most women who have an HPV infection do not have any
symptoms and most infections will go away without treatment. Genital warts are often the only visible sign that a person is
infected. Persistent HPV infections in women can lead to cancers of the cervix, vagina, vulva, anus and certain cancers of the head
and neck, such as throat and back of mouth cancers.
HPV vaccination is one of the top ways to help protect yourself against certain HPV-related cancers and diseases. Regular Pap tests are the best way to find abnormal cervical cells early and treat them before they develop into cervical cancer. A Pap test is a simple screening method that detects cell changes in the cervix. The majority of abnormal Pap tests are caused by HPV.
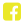
HPV in women can lead to:
View image
(WARNING: Graphic content)
Symptoms can include abnormal vaginal bleeding, pain during intercourse, increased vaginal discharge, pain in the pelvic area or lower back, weight loss, lack of energy and shortness of breath
Photograph courtesy of Dr. Michel Roy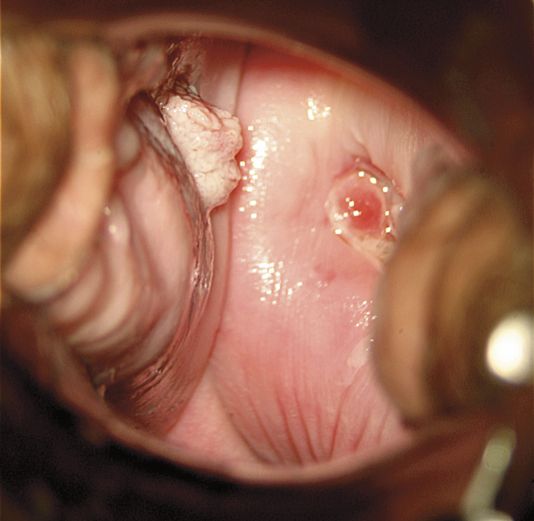
View image
(WARNING: Graphic content)
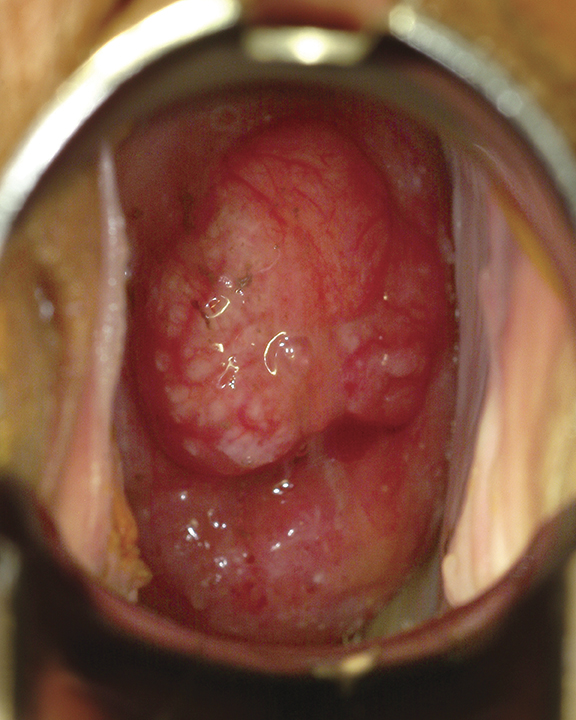
Often shows no signs. Can cause itchiness or burning that does not go away, pain in the pelvic area, abnormal vaginal bleeding, difficulty urinating or painful intercourse
Photograph courtesy of Dr. Michel Roy
View image
(WARNING: Graphic content)
Symptoms can include a lump or sore in the head and neck area that does not heal, a sore throat that doesn’t go away, white or red patches in the mouth, difficulty swallowing or a change in the voice.
Photograph courtesy of Dr. Anthony Zeitouni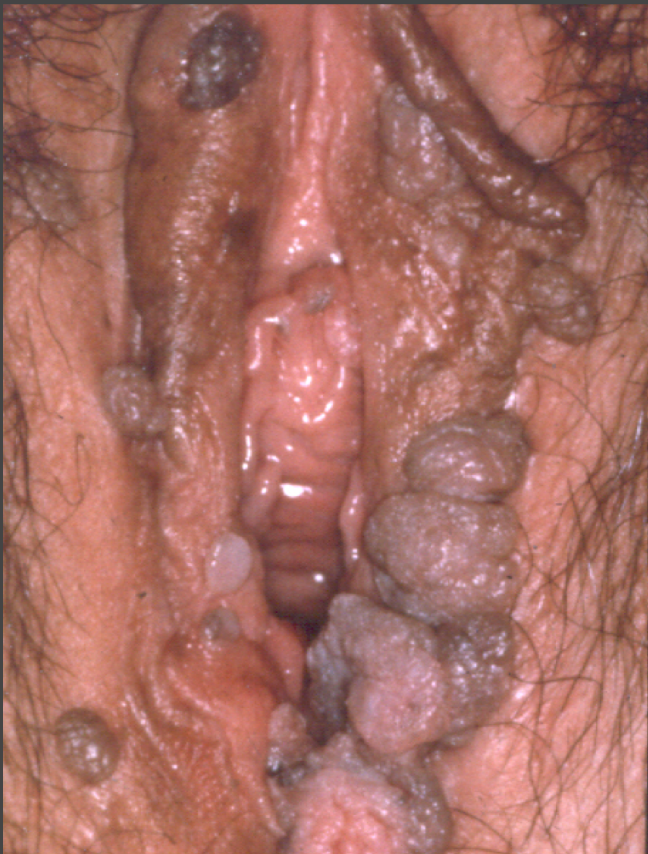
View image
(WARNING: Graphic content)
Small, cauliflower-like growths that may itch or burn. They can be raised or flat, small or large, and grow alone or in clusters.
Photograph courtesy of Dr. Alex Ferenczy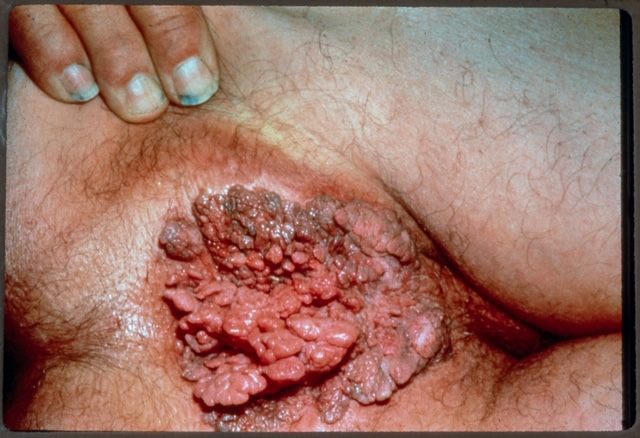
View image
(WARNING: Graphic content)
Symptoms can include anal bleeding, difficulty passing stools, pain, lumps, itching or discharge.
Photograph courtesy of Dr. Alex FerenczyHow to help reduce your risk
HPV vaccination is one of the top ways to help protect yourself against certain HPV-related cancers and diseases.
You can also help reduce your risk of HPV infection by:
Limiting your number of sexual partners
Using a condom correctly and consistently
Not smoking
Help protect yourself against certain HPV-related cancers and diseases
Find out how you can get your
GARDASIL®9
vaccine in 3
simple steps!
You can also begin the process by connecting with a
virtual healthcare provider and finding a vaccination site near you.
Frequently asked questions
Yes. GARDASIL®9 can be administered in individuals ages 9 to 45, to help protect against infection caused by HPV types 6, 11, 16, 18, 31, 33, 45, 52 and 58 and the following diseases caused by HPV:
- Cervical cancer (cancer of the lower end of the uterus or womb) caused by HPV types 16, 18, 31, 33, 45, 52 and 58
- Vulvar (the outside of the female genital area) and vaginal cancers caused by HPV types 16, 18, 31, 33, 45, 52 and 58
- Certain head and neck cancers, such as throat and back of mouth cancers caused by HPV types 16, 18, 31, 33, 45, 52 and 58. GARDASIL®9 has been issued market authorization with conditions for this indication pending the results of trials to verify its clinical benefit
- Anal cancer caused by HPV types 16, 18, 31, 33, 45, 52 and 58
- Genital warts caused by HPV types 6 and 11
- Abnormal and precancerous cervical lesions (changes in cells of the cervix that have a risk of turning into cancer) as found in a Pap test caused by HPV types 6, 11, 16, 18, 31, 33, 45, 52 and 58
- Abnormal and precancerous vaginal, vulvar and anal lesions caused by HPV types 6, 11, 16, 18, 31, 33, 45, 52 and 58
For more information about GARDASIL®9, talk to your healthcare professional.
GARDASIL®9 helps prevent the diseases caused by some types of HPV but will not treat them. If you are already infected with one type of HPV contained in the vaccine, GARDASIL®9 will help protect you against the other eight types.
Talk to your healthcare professional for more information.
Yes. HPV is a common virus. The majority of sexually active people will catch HPV during their lifetime. Many people who have HPV may not show any signs or symptoms. This means that they can transmit (pass on) the virus to others without knowing it. Each partner in a sexual relationship may carry the infection for many years without knowing it because there are often no visible symptoms.
You can be at risk even if you have only one sexual partner because your partner may have had other partners in the past.
Talk to your healthcare professional for more information.
Have additional questions? Check out our FAQ page.