HPV-related cancers & diseases
HPV infection can lead to several HPV-related cancers and diseases in men and women.
View image
(WARNING: Graphic content)
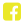
Symptoms can include abnormal vaginal bleeding, pain during intercourse, increased vaginal discharge, pain in the pelvic area or lower back, weight loss, lack of energy and shortness of breath.
Photograph courtesy of Dr. Michel Roy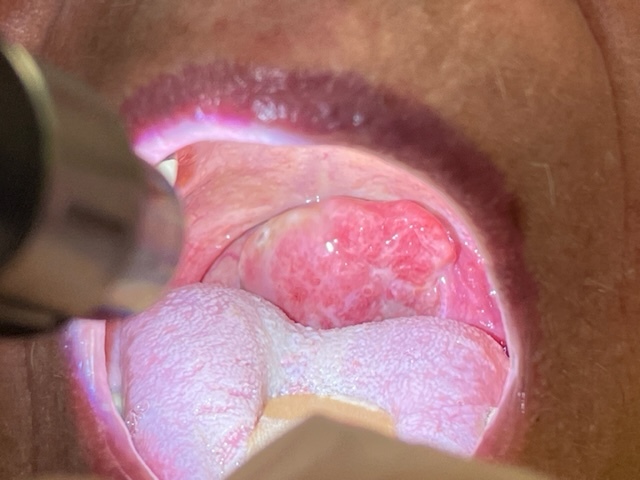
View image
(WARNING: Graphic content)
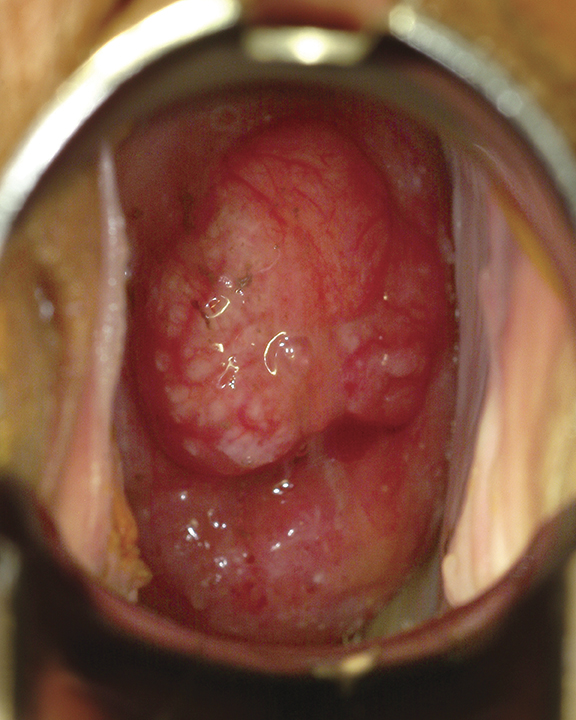
Symptoms can include a lump or sore in the head and neck area that does not heal, a sore throat that doesn’t go away, white or red patches in the mouth, difficulty swallowing or a change in the voice.
Photograph courtesy of Dr. Anthony Zeitouni
View image
(WARNING: Graphic content)
Symptoms can include anal bleeding, difficulty passing stools, pain, lumps, itching or discharge.
Photograph courtesy of Dr. Alex Ferenczy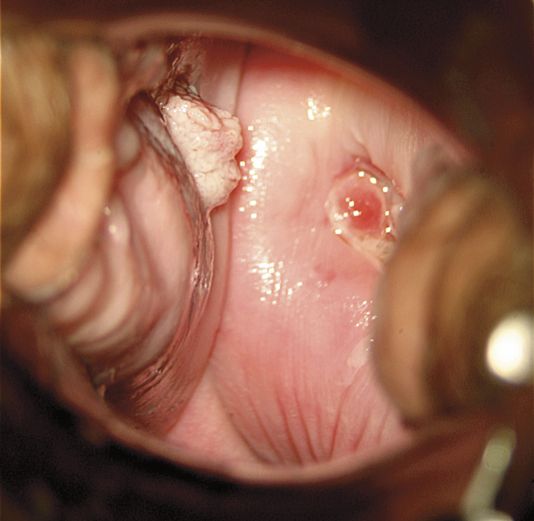
View image
(WARNING: Graphic content)
Often shows no signs. Can cause itchiness or burning that does not go away, pain in the pelvic area, abnormal vaginal bleeding, difficulty urinating or painful intercourse.
Photograph courtesy of Dr. Michel Roy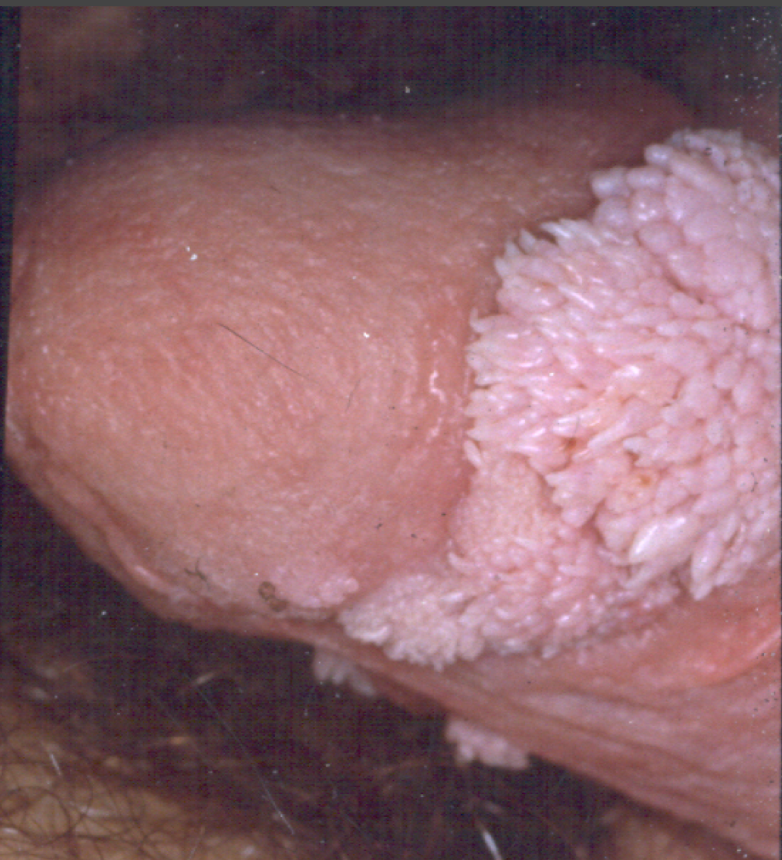
View image
(WARNING: Graphic content)
Small, cauliflower-like growths that may itch or burn. They can be raised or flat, small or large, and grow alone or in clusters.
Photograph courtesy of Dr. Alex Ferenczy
View image
(WARNING: Graphic content)
Can appear as a raised, wart-like or flat growth on the head or foreskin of the penis and can be painful and inflamed, with some itching and burning in the area.
Photograph courtesy of Dr. Alex FerenczyAnal cancer, or cancer of the anus, is rare but increasing.
In 2016, 200 men were diagnosed with anal cancer in Canada.
HPV is the leading cause of genital warts.
HPV types 6 and 11 cause over 90% of genital warts in men and women.
HPV IS RESPONSIBLE FOR NEARLY 100% OF CERVICAL CANCER CASES
Cervical cancer will kill an estimated 380 Canadian women in 2022.*
Learn more about HPV-related cancers and diseases.
WHAT IF YOU COULD HELP PREVENT CERTAIN HPV-RELATED CANCERS WITH A VACCINE?

IN MEMORY OF CHRISTA†
Even if you think you’re too young, you could still be at risk. This is Christa’s story. Diagnosed with cervical cancer at age 33.

MEET HEATHER†
Even if you’re a healthy new mom, you could still be at risk. This is Heather’s story. Diagnosed with cervical cancer at age 27.